


Nakalele Point is a land mass on the eastern edge of the northern tip of the island of Maui in the state of Hawaiʻi. In Hawaiian, Nakalele or Nā-kālele means "the leaning". The Point is known for its blowhole and has become notable for its dangerous conditions when waves crash in. The point and blowhole are located just east of Poelua Bay.

David Potts, right, was on the Hawaiian island fro some down time with his fiancee Tika Hick.
16th July 2011 - The fiancée of the Northern California man who was sucked into a Maui blowhole to his death has spoken out to say there should have been signs warning people of the dangers. Tika Hick said that 44-year-old David Potts vanished into the ocean during a vacation to enjoy some time in the Maui sun before she undergoes a double mastectomy next week following a recent breast cancer diagnosis. Eyewitness accounts from tourists who were there said Potts was dancing around inches from the hole's opening and playing in the sprays of water shooting high into the sky when he disappeared. Hick disputed that description and took local officials to task for not posting warning signs at the site. She was not at the blowhole at the time, but said her brother and sister-in-law were there.

Image right - The only signage at the Nakalele blowhole is a quarter-mile away - a handmade sign that cautions visitors, "Blowhole, park and walk at your own risk."

Blowhole
Nakalele Point is famous for a blowhole which produces powerful geyser-like water spouts with the waves and tides. Water spewed from the blowhole can rise as high as 100 feet in the air. Visitors to the site should never stand between the blowhole and the ocean, and visitors should never turn their backs on the ocean as rogue waves could cause injury at any time.

INSANE HAWAII MAUI BLOWHOLE! LOOK DOWN THE HOLE! RIPPIN!!!

David Potts with fiancee Tika Hick in Hawaii..
INSANE HAWAII MAUI BLOWHOLE! LOOK DOWN THE HOLE! RIPPIN!!!

Tragedy: Rocco Piganelli took a photo of his daughter and friends in front of the blow hole seconds before David Potts was sucked to his death with no chance of escaping the deadly hole.
He slipped because it was slippery,' said a sobbing Hick. The incident has served as another tragic reminder of the dangers lurking along undeveloped stretches of Hawaii's shoreline. Online travel sites warn of the rocky cliffs near the blowhole and its unpredictable eruptions. The blowhole was created by pounding surf that undercut and wore away a lava shelf. Every wave pushes water and air through the hole, creating an eruption similar to a geyser. Then as the water retreats, it creates a strong vacuum-like effect. Maui County officials said the blowhole appears to be on private land, according to property records, but were still in the process of verifying that. The county said people were continuing to visit the area, despite being told of what happened to Potts.

Moments from death, David Potts teeters over the edge of the deadly blow hole just before a freak wave washes him inside never to escape..
The state is researching the ownership of the blowhole, said Deborah Ward, spokeswoman for the state Department of Land and Natural Resources. The Hawaii Tourism Authority asked Maui Land & Pineapple for permission to post warning signs near the blowhole, which the company granted, Ho said. She said publications that promote the blowhole as a destination present constant challenges for the company. "We don't have the resources to fence our entire property line and by state law we have to provide public access to the shoreline." Maui Police Lt. Chad Viela, who is overseeing the investigation, said this is the first time he's heard of someone falling into the hole, which has an opening that's about 3-feet wide. It's a popular tourist destination, he said, among visitors wanting to explore the undeveloped, sparsely populated terrain of western Maui's northern tip.
We urge all visitors to the location to please use caution an as obvious danger exists at or near the blowhole,' the county said in a statement, also noting that it and the Maui Visitors Bureau do not promote the area as a tourist spot. There are still questions about who owns the land at the site of the blowhole - and who could be the target of a possible lawsuit over the episode. The county said records indicate the property is owned by Maui Land & Pineapple Company. Kalani Ho, the company's land and property manager, said the blowhole is on public property because it is on the shoreline. 'The blowhole is below the high-water mark,' she said. 'State land is below the high-water mark and obviously that's in the water.'

David Potts body was never found, and Tika had to make the long flight home without him. Now she is left to raise their infant son, Indigo, on her own, rejoicing and grieving as she sees the man she loves in the face of their child.

Hālona Blowhole is a rock formation and a blowhole on the island of Oahu, Hawaii off of Hanauma Bay at Hālona Point overlooking the Pacific Ocean. In Hawaiian hālona means "lookout".
'The ocean conditions are much more treacherous out that side of west Maui,' he said. "'Visitors just don't know the dangers." The last time someone died at a blowhole in Hawaii was 2002 when an 18-year-old from Sylmar, Calif., fell into the Halona blowhole on Oahu and drowned. In the latest case, Hick said she visited the site on Maui before leaving Hawaii and paid tribute to the man she was supposed to marry. 'We put flowers in the water to say goodbye and asked Hawaii to take care of him," she said, "and to take care of me and our son.'

The Hālona Blowhole on Oahu, Hawaii

The Hālona Blowhole on Oahu, Hawaii

Explosive Ocean Blow hole: Must see!!
Explosive Ocean Blow hole: Must see!! Hālona Blowhole Oahu.
A lighthouse was erected around 1908 at Nakalele Point. It originally consisted of a 40 feet (12 m) high wooden mast on top of which a temporary light was placed. By 1910, an actual dwelling was built with boxlike platform on its roof for a fixed white light. In 1922, the light was automated so that it would flash. The lighthouse is currently owned by the United States Coast Guard.

Hālona beach cove.. A fantastic holiday destination..


The lighthouse was erected around 1908 at Nakalele Point..
On windy days when the tide is high, the ocean breeze sends the waves rolling on to the shore where the rock formation then shoots sea spray high into the air through the cave acting like a geyser. The blowhole is most active when the tide is high and the winds are strong, and it can shoot sea spray up to thirty feet high in the air. Hālona Point is a tourist spot, with visitors coming for the scenery, the beach at the cove, and in the winter as a spot to go to see humpback whales (whose blowholes are not to be confused with this formation) or Honu turtles (Hawaiian Green Sea Turtles). The blowhole is perhaps the most popular rock formation of its kind found in Hawaii.

A Lava tube at Hālona beach cove

Hawaiʻi is the home to five species of sea turtles. Olive ridleys, loggerheads and leatherbacks are usually only encountered in deep offshore waters, and hawksbills are so few in number (<100 nesting females exist in the Main Hawaiian Islands) that they are rarely seen by most people. But it’s common for snorkelers and divers on all the islands to see the honu (green sea turtle) in near shore waters. 96% of Hawaiʻi’s green sea turtles nest in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands, Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the largest fully protected conservation area under the U.S. flag.
Unfortunately, honu (green turtles) are impacted by near shore fisheries interactions, and are suffering from a disease called fibropapillomatosis. This herpes-family virus causes the growth of white to blackish, cauliflower-like tumors. These grow on the soft tissues of the turtle’s body, internally and externally, and inhibit foraging, breathing, mobility and digestion. It is unclear what causes this disease, but research is ongoing worldwide to find a cure.
It can be deadly when sea turtles get hooked or entangled in fishing line. These interactions can cause starvation (if the hook doesn’t allow the turtle to close its mouth), limb amputation (if the line gets wrapped so taught that it cuts through the skin and bone) or drowning (if the line or hook gets caught on the reef and prevents the turtle from surfacing to breathe). “Basking” (resting) behavior is becoming more common all around Hawai‘i and is an exciting way to watch green sea turtles, but it is important that people or dogs don’t scare the turtles back into the ocean. The presence of people doesn’t allow for turtles to rest. Hawaii Wildlife Fund (HWF) recommends staying 15 feet (5 meters) away and don’t block their access either to or from the ocean. Please avoid making loud noises and please do not use flash photography.

Mermaid Caves and Nānākuli Beach Park | Best Beaches on Oahu | Things to do in Hawaii
Mermaid Caves and Nānākuli Beach Park | Best Beaches on Oahu | Things to do in Hawaii

Nicki Minaj - Starships (Explicit) (Official Video)
Nicki Minaj - Starships (Explicit)
Hālona Cove was the site of the sex scene between Deborah Kerr and Burt Lancaster in the 1953 film From Here to Eternity, and also between Drew Barrymore and Adam Sandler in the movie 50 First Dates. In 2012, the beach was featured in the music video for Nicki Minaj's "Starships". The blowhole was the location for a scene in Jurassic World: Fallen Kingdom...

What Makes Hawaii's Green Sea Turtles Unique?
What Makes Hawaii's Green Sea Turtles Unique?

A Harvard professor says aliens visited us in 2017 and warns more are coming — but a bunch of Hawaiians say they’re already here. Multiple people witnessed and videotaped a bright blue, glowing, oblong unidentified flying object hovering above the skies of Oahu last Tuesday (December 29th 2020) — before it nosedived into the ocean, prompting them to call the Federal Aviation Administration and 911. The sighting occurred at 8:30 in the evening and videos show a strange mass both in the sky and water.
.jpg)


Bright blue UFO seen crashing into ocean near Hawaii prompts calls to 911, FAA | ABC7
Misitina Sape, who captured one of the videos in Nanakuli, can be heard saying, “Something is in the sky. What is that?,” according to Hawaii News Now. Another woman named Moriah also saw the object passing over Princess Kahanu Estates and told HNN: “I look up and then I was like, ‘Oh s—!’ I started calling my husband and them because they were all in the garage. I was like, ‘Hey. Come look up there. See if you see what I see.’ They all said, ‘Yeah!’ I don’t know what it was … This one was going so fast.”
Bright blue UFO seen crashing into ocean near Hawaii prompts calls to 911, FAA | ABC7

Multiple UFOs Sighted Over Waianae, Oahu, Hawaii ( May 31, 2021 )
Officials from the Federal Aviation Administration told HNN there were no aircraft incidents or accidents in the area at the time. But multiple witnesses reported seeing a large blue object fall out of the sky and into the ocean. Moriah followed the UFO — which was silent and “larger than a telephone pole” — for a mile until it dropped into the ocean. In one of her videos, she is heard saying: “(It) went land in the water. Whatever it is.” After officers arrived, Moriah spotted a second light, which was white, coming from the same direction as the blue lit object.
Multiple UFOs Sighted Over Waianae, Oahu, Hawaii ( May 31, 2021 )
“My husband went ‘Look up’ and he seen the white one coming,” she told HNN. “The white one was smaller. Was coming in the same direction as the blue one.” A spokesperson for the Honolulu police told HNN there was no information about the object, and FAA spokesperson Ian Gregor said the agency received a report from police Tuesday night about a possible plane down in the area “but had no aircraft disappear off radars. And no reports of overdue or missing aircraft.”

Beijing — A Chinese zoo has been forced to deny that its sun bear is actually a human in a costume, after video of one standing on its hind legs raised online accusations of a furry imposter.
A video clip of a bear rearing up and interacting with a group of people at a zoo in eastern Hangzhou city went viral on Chinese social media.

Zoo Says Bear Standing Upright Is Not a Person in a Costume
Zoo Says Bear Standing Upright Is Not a Person in a Costume.
Many users posted comments doubting that the bear was real, with some alleging that its bipedal posture and wrinkled skin suggested that it was actually a human in costume. But the zoo dismissed the rumours, saying in a statement written from the bear's perspective on Sunday that the animal was real and its detractors "really don't understand me". "The zoo director called me after work yesterday and asked if I'd been slacking off by finding a two-legged beast to replace me," the bear, named Angela, said in the statement. "Some people thought the way I stand up looks too human... so I will stress again: I'm a sun bear!" Native to Southeast Asia, sun bears are named for a patch of bright orange or cream-coloured chest fur that stands out against the rest of its jet-black coat. It is the smallest bear - about the size of a large dog - and is listed as a vulnerable species due to deforestation and the global wildlife trade. Other Chinese zoos have previously been accused of stocking their enclosures with animals that are not what they seem - including a hairy dog passed off as an "African lion" and a pool filled with penguin-shaped balloons.


.jpg)

Remi Lucidi—who was known on Instagram for climbing tall and dangerous structures around the world—reportedly died on July 27th after falling from the 68th floor of a skyscraper in Hong Kong. He was 30.

The French daredevil was last seen knocking on a window from the outside of a penthouse suite, startling a maid inside the high-rise, per the South China Morning Post. The maid then called police, who arrived to find Lucidi's body at a nearby patio along with his identification and a video camera containing footage of extreme sports, according to the publication. Authorities told the local outlet that Lucidi gained entry after telling a security guard that he was there to visit a friend on the 40th floor. He proceeded to enter an elevator, with surveillance footage capturing him arriving on the 49th floor. From there, police said the stunt influencer made his way to the top floor, where a door was found to have been forced open.

What could of happened to Remi Lucidi, If he was at the top of the building indicated by a green arrow he could of rested as there is sufficient space.. He could also have got back into the building from the top as from the image there are doors and windows and another apartment rests on the top. He tapped on a window for someone to let him inside and I don't understand that he slipped and fell..
The Tregunter Towers (Chinese: 地利根德閣) is a complex of three residential buildings located in The Peak on Hong Kong Island, Hong Kong. All three highrises, named Tregunter 1 (地利根德閣第一座), Tregunter 2 (地利根德閣第二座), and Tregunter 3 (地利根德閣第三座).
Tregunter 1 and 2 were developed by Hong Kong Land, designed by Chun Wah Nam Architect and constructed by John Lok and Partners, both completed in the year 1981 and both buildings have similar floor counts at 34 and 33 respectively. The last building of the complex, Tregunter 3, was completed in 1993 or twelve years after Tregunters 1 and 2. The (Tregunter) tower 3 was designed by Rocco Yim Architects Ltd and constructed by Hip Hing Construction Co. Ltd. Tregunter 3 stands significantly taller than the first two buildings of the complex at 220 m (721 feet) with 66 stories. The top floor of Tregunter 3 stands 327 m (1,073 ft) above sea level. Upon its completion, Tregunter 3 was the world's tallest all-residential building, taking the title from the Lake Point Tower in Chicago. Tregunter 3 held this distinction until the completion of Trump World Tower in 2001. Standard apartments range from 1600 square feet to over 2500 square feet in size.
The three Tregunter towers share the common facilities which often regarded as one of the most complete in the area especially for older buildings. The common facilities include a clubhouse, an outdoor tennis court and an outdoor swimming pool. Within the clubhouse, there are other sport facilities such as badminton, squash, table tennis, basketball, weight training, aerobics, etc. The clubhouse also has a restaurant, and function rooms reserved for the use by the Tregunter residents. There are also two shuttle bus routes between the complex and Central and the complex and Admiralty.
Images below are AI generated and do not represent exactly what happened..






The Crooked House - National Wonders
The Crooked House was a pub and restaurant in South Staffordshire, England. Its name and distinctive appearance are the result of 19th-century mining subsidence, which causes one side of the building to be approximately 4 feet (1.2 m) lower than the other. The building is located near to Himley between Dudley and Telford, on the border of Staffordshire and the West Midlands. In July 2023, it was sold for "alternative use" and it was reported that the building was unlikely to reopen as a pub. The following month it caught fire.
The Crooked House - National Wonders

The Crooked House was built in 1765 and was originally a farmhouse. During the early 19th century, mining in the area caused one side of the building to begin gradually sinking. By c. 1830 it was a public house called the Siden House, siden meaning "crooked" in the local Black Country dialect. The building was later renamed the Glynne Arms after the local landowner, Sir Stephen Glynne, on whose land it stood.
The Crooked pub from inside is very crooked indeed..

The building was condemned as unsafe in the 1940s and was scheduled for demolition. Wolverhampton and Dudley Breweries purchased the pub and rescued it by making the structure safe using buttresses and girders to retain its lopsided appearance. The building was put up for sale in 2023. On 25th June, it was the subject of a burglary causing over £10,000 of damage. (A few pints too many in this pub might cause a problem or too..)

On the evening of 5th August 2023, a fire broke out in the pub; the following day it was reported that the interior had been gutted and photographs showed that the roof had been destroyed. Appliances from Staffordshire Fire and Rescue Service and the West Midlands Fire Service were initially unable to access the site as the only road serving the pub had been blocked.
Optical illusions
The building's leaning walls give rise to optical illusions, as with a gravity hill. These include glasses slowly sliding across "level" tables and a marble appearing to roll uphill.
.jpg)




Marbles Roll Uphill At Crooked Pub
An update post on the pub’s Facebook page on 27 July said: “The Crooked House has been sold. Unlikely to open its doors again. Marston’s have sold the site to a private buyer for alternative use, that is all we know. This is just to update the page so nobody makes any wasted journeys to the site.”
Andy Street, mayor of the West Midlands, said there were “a lot of questions” surrounding the fire.
“I’m sure the authorities will get to the truth,” he said. “Today all we can say is what a tragedy, and I sincerely hope this iconic Black Country landmark can be restored and preserved.”
Marbles Roll Uphill At The Crooked Pub -


The charred remains of the Crooked House pub. An investigation is under way into the cause of the blaze. Photograph: Stop Press Media/Alamy Stock Photo - The Crooked public house is no more..
Firefighters were called on Saturday night (5th August 2023) to the Crooked House pub, in Himley near Dudley in the West Midlands, which gained its name after it started sinking into the ground due to mining subsidence in the area.
Roads around the area were closed as smoke and flames poured from the Grade II-listed building.
A spokesperson for Staffordshire fire and rescue service said several crews attended a severe fire at the pub and tried to extinguish the blaze.
Staffordshire police said they were working with fire investigators to establish the cause of the fire. A spokesperson for the force said: “Fire investigators are inspecting the scene this morning 6th August 2023 and officers are making local inquiries to secure any information that might help the investigation.” A petition to save the pub from redevelopment, launched on 29 July, had attracted more than 3,500 signatures.

Devils Hole is a geologic formation located in a detached unit of Death Valley National Park and surrounded by the Ash Meadows National Wildlife Refuge, in Nye County, Nevada, in the Southwestern United States. Devils Hole is habitat for the only naturally occurring population of the endangered Devils Hole pupfish (Cyprinodon diabolis). The 40 acres (16 ha) unit is part of the Ash Meadows complex, an area of desert uplands and spring-fed oases that was designated as a National Wildlife Refuge in 1984.

Death Valley National Park is an American national park that straddles the California–Nevada border, east of the Sierra Nevada. The park boundaries include Death Valley, the northern section of Panamint Valley, the southern section of Eureka Valley and most of Saline Valley. The park occupies an interface zone between the arid Great Basin and Mojave deserts, protecting the northwest corner of the Mojave Desert and its diverse environment of salt-flats, sand dunes, badlands, valleys, canyons and mountains. Death Valley is the largest national park in the contiguous United States, as well as the hottest, driest and lowest of all the national parks in the United States.
Death Valley National Park..

It contains Badwater Basin, the second-lowest point in the Western Hemisphere and lowest in North America at 282 feet (86 m) below sea level. More than 93% of the park is a designated wilderness area. The park is home to many species of plants and animals that have adapted to the harsh desert environment including creosote bush, Joshua tree, bighorn sheep, coyote, and the endangered Death Valley pupfish, a survivor from much wetter times. UNESCO included Death Valley as the principal feature of its Mojave and Colorado Deserts Biosphere Reserve in 1984.

A series of Native American groups inhabited the area from as early as 7000 BC, most recently the Timbisha around 1000 AD who migrated between winter camps in the valleys and summer grounds in the mountains. A group of European Americans, trapped in the valley in 1849 while looking for a shortcut to the gold fields of California, gave the valley its name, even though only one of their group died there. Several short-lived boom towns sprang up during the late 19th and early 20th centuries to mine gold and silver. The only long-term profitable ore to be mined was borax, which was transported out of the valley with twenty-mule teams. The valley later became the subject of books, radio programs, television series, and movies. Tourism expanded in the 1920s when resorts were built around Stovepipe Wells and Furnace Creek. Death Valley National Monument was declared in 1933 and the park was substantially expanded and became a national park in 1994.

National Park Service rangers are photographed next to a digital display of an unofficial heat reading at Furnace Creek Visitor Center in Death Valley, California, on Sunday 16th July 2023.
Long the hottest place on Earth, Death Valley put a sizzling exclamation point on Sunday on a record warm summer that is baking nearly the entire globe by flirting with some of the hottest temperatures ever recorded, meteorologists said.
Temperatures in Death Valley, which runs along part of central California’s border with Nevada, reached 128F (53.3C) on Sunday at the aptly named Furnace Creek, the National Weather Service said.
The hottest temperature ever recorded on Earth was 134F (56.7C) in July 1913 at Furnace Creek, said Randy Ceverny of the World Meteorological Organization, the body recognized as keeper of world records. Temperatures at or above 130F (54.4C) have only been recorded on Earth a handful of times, mostly in Death Valley.

'In an oven': visitors react to Death Valley heat
'In an oven': visitors react to Death Valley heat.

Devils Hole is the only natural home of the endangered Devils Hole Pupfish.
Kim Stringfellow 2019..
Devils Hole is a geothermal pool within a limestone cavern in the Amargosa Desert in the Amargosa Valley of Nevada, east over the Amargosa Range and Funeral Mountains from Death Valley. It is at an elevation of 730 m (2,400 ft) above sea level and the water is a constant temperature of 33 °C (91 °F). The surface area of Devils Hole is about 22 m long by 3.5 m wide (72 ft long by 11.5 ft wide). Approximately 0.3 m (1.0 ft) deep on one end of Devils Hole is a small rock shelf of 3.5 by 5 m (11 by 16 ft). The dissolved oxygen of the water is 2.5–3.0 ppm up to around 22 m (72 ft) in depth, though the shallow shelf can have dissolved oxygen levels as high as 6.0–7.0 ppm in June and July.

Funeral Mountains..
A viewing platform overlooks the hole.
Devils Hole branches into caverns at least 130 m (430 ft) deep, whose bottom has never been mapped. According to geologists, the caves were formed over 500,000 years ago. The pool has frequently experienced activity due to far away earthquakes in Japan, Indonesia, Mexico, and Chile, which have been likened to extremely small scale tsunamis.

The calm, carbonate-rich and oxygen-poor water of Devils Hole is a constant 33.5–34°C (93°F) in the deeper reaches of the cave and is often even warmer in the shallows. This combination creates a challenging environment for the tiny blue Devils Hole pupfish! These fish subsist on algae, invertebrates, and other micro-organisms found on a shallow rock shelf within the pool. The water level in Devils Hole was protected by the United States Supreme Court in 1976 to help ensure the ongoing survival of this unique fish. With only about 100–180 individuals remaining in the wild, scientists continue their efforts to conserve the species for this and future generations to learn from and enjoy.

Below the surface pool, Devils Hole descends approximately 160 feet (50 m) through what is termed the "main chamber" before reaching a narrow opening referred to as the 'funnel'. Through this opening lies a much larger chamber of the cavern system known as Acree's Chasm. Acree's Chasm is approximately 300 feet (91 m) in length, 40 feet (12 m) in width, and has a bottom approximately 260 feet (80 m) below the surface.
Immediately after passing the funnel into Acree's Chamber, a narrow side tube can be found to a diver's left. This side tube proceeds approximately 90 feet (27 m) upward to a chamber with an air pocket, named Brown's Room. The tube leading to Brown's Room has at least 2 offshoots, the higher of which leads to a dead-end filled with a small air pocket, and the lower of which joins with additional tubes descending from Brown's Room. If the diver instead descends through Acree's Chamber, the first notable landmark is a rocky shelf termed the "lower ledge", around 100 feet (30 m) below the entrance to the chamber. The bottom of Acree's Chamber lies around 260 feet (79 m) below the surface, but is not flat. Instead, a portion of the chamber floor descends below this lower shelf; a gradual funnel leads to a hole in the bottom of the chamber featuring a strong current. The hole, later termed the ojo de agua, is 315 feet (96 m) below the surface and just large enough for a diver with equipment to fit through.

A sign at Devils Hole death Valley Amargosa Valley Nevada..

On The Trail: Devils Hole

Devil’s Hole and the Tragic Disappearance of Two Teens in 1965
Devil’s Hole and the Tragic Disappearance of Two Teens in 1965
On The Trail: Devils Hole..

Devil's Hole Mystery - Missing Divers, Water Babies And Charles Manson?
Devil's Hole mystery - Missing Divers - Water Babies and Charles Manson?

Nevada's Mysterious Devil's Hole: Center of Terrifying Stories and Legends?
Nevada's mysterious Devil's Hole - Center of terrifying stories and legends..
Divers have explored as far as 436 feet down and could see another 150 feet below them, and experts suspect it could go 900 feet down or more. They don't know for sure because there hasn't been an expedition to reach the bottom. Some suspect the water connects with locations across the world, due to how Devils Hole reacts to seismic events in other countries. Low oxygen levels and elevated levels of nitrogen demand expert divers for this cave system.. A rebreather is necessary if the diver is going down deep as oxygen turns poisonous before 180 feet in some cases.. There are depth limitations too, as nitrogen becomes narcotic the deeper you go. This becomes increasingly debilitating, so the maximum depth for recreational diving is 130 feet (40 m). Air itself becomes toxic as we go beyond 184 feet (56 m). Nitrogen is safe to breathe only when mixed with the appropriate amount of oxygen.

Oxygen will start to become toxic at 1.6 ATA (atmospheres absolute) for some people and will become toxic for everyone at 2.8 ATA. It doesn’t become toxic immediately, it occurs over time, but at 2.8 ATA it will happen eventually.
So at a depth of about 18′ it may become toxic for some but not for others. At 60′ it will be toxic, but not at once. Commercial divers must take an O2 toxicity test where we go to 60′ in a chamber and breathe pure O2 for 30 minutes to make sure you are not sensitive to O2. Also treatment tables (what you do if you get decompression sickness) have divers breathe pure O2 at 60′ for 20 minutes then take a 5 minute break breathing air, then go back to breathing O2.

The Hole's layout creates the ideal balance for the pupfish to survive. Sunlight keeps the water warm, and a shelf near the water system's entrance helps algae form on the limestone walls. The pupfish thrives in this shallow shelf because it can feed on the algae. The population fluctuates from about 100 to 500 fish throughout the year. They don't have to worry about cramped conditions because each pupfish is less than 1-inch long. (Cyprinodon diabolis) critically endangered and can only be found at Devils Hole cave Nevada..
The pupfish consumes nearly every available food resource at Devils Hole, including beetles, snails, algae, and freshwater crustaceans, with diet varying throughout the year. It is preyed on by the predaceous diving beetle species Neoclypeodytes cinctellus, which was first observed in Devils Hole in 1999 or 2000. Reproduction occurs year-round, with spikes in the spring and fall. Females produce few eggs, though, and the survivorship from egg to adult is low. Individuals live 10–14 months. As a byproduct of this alternate respiration method, the fish produces ethanol.

Although pupfish have been found as deep as 24 metres (80 ft), their numbers are most dense above depths of 15 m (49 ft). They depend on the shallow shelf for spawning as well as for much of their diet which primarily consists of diatoms. Natural threats from flash floods to earthquakes have been known to disrupt this fragile ecosystem, but in the 1960s and 1970s, the major threat was groundwater depletion due to agricultural irrigation. After vandalism resulted in the death of a pupfish in 2016, the National Park Service added additional barbed wire to the top of the fences surrounding Devils Hole, also installing more motion sensors and video cameras.

Devil's Hole is so deep that it acts as a natural seismograph. Earthquakes from across the planet have produced tsunamis in the narrow opening. In one instance, tremors from Indonesia caused massive waves to oscillate 6 feet higher than the natural water level in the Hole.
Due to the fear of extinction in the 1960s and 1970s, several measures were taken to create multiple populations of the pupfish outside of Devils Hole to safeguard the species, which is known as ex situ conservation. Some of these measures, such as transplanting the fish into nearby natural springs, quickly failed. The fish disappeared, though one population at Purgatory Spring was destroyed by biologists, as the fish were misshapen and no longer looked like Devils Hole pupfish. Two attempts were made at this time to establish aquaria populations, one at Steinhardt Aquarium and the other at Fresno State College, though these also failed. A number of artificial "refugia" consisting of concrete tanks approximating conditions in Devils Hole were attempted to ensure the species' survival should the natural population at Devils Hole die out. The Hoover Dam Refugium for Endangered Desert Fish was established in August 1972, with the first twenty-seven pupfish translocated in October 1972. The Hoover Dam Refugium was successfully maintained for several years and reached a population of several hundred, though the sex ratio was highly skewed towards males with as many as three males per female. In 1985 or 1986, a component of the water supply system failed, however, killing many of the fish. Nearly all the remaining fish were killed by October 1986 when an additional failure caused the water temperature to drop drastically. The lone surviving fish was then removed. In 1973, a second refugium was established at Ash Meadows National Wildlife Refuge (AMNWR), the Amargosa Pupfish Station, also known as the School Springs refuge. From the founding population of twenty-five fish, it remained at several dozen individuals until a power failure in August 1984 disrupted the water flow, reducing the population to seven. The population increased to 121 by October 1987. In 1990, a third refugium was constructed, also at AMNWR, called Point of Rocks refuge.

In May through August 2006, two pupfish from Devils Hole and five from the Hoover Dam Refuge were transferred to a Las Vegas Strip casino aquarium at Mandalay Bay with the hope of understanding how to breed the species in aquaria. Propagation efforts at Mandalay Bay failed, and by April 2007 all individuals had died or been transferred. Also in 2006, six younger pupfish were moved from Devils Hole to the Willow Beach National Fish Hatchery in Arizona. Additionally, the eighteen remaining individuals from the Hoover Dam refuge were moved to Willow Beach. While early breeding efforts appeared successful and four larvae survived to adulthood, all individuals had died by December 2006, possibly from a form of leukemia.

Willow Beach National Fish Hatchery in Arizona
In the early 2010s, a full-scale replica of the upper 6.7 m (22 ft) of Devils Hole was built at the new Ash Meadows Fish Conservation Facility (AMFCF),[60] resulting in a 380,000 L (100,000 U.S. gal) tank. Located less than a mile away (36°25′25″N 116°18′21″W), this refuge closely mimics the natural Devils Hole, including water chemistry, spawning shelf, and natural sunlight. It intentionally differs, however, in temperature and dissolved oxygen content. The temperature is 2–3 °C (3.6–5.4 °F) cooler than that of Devils Hole and the dissolved oxygen content is doubled in attempts to reduce thermal and respiratory stress on the fish.

Main Chamber going down at Devil's Hole Nevada..
The population of Devils Hole pupfish at AMFCF was created by taking eggs from Devils Hole. However, eggs are only removed at times of the year when it is unlikely that they would develop into mature adults, such as in the winter. It is thought that egg removal during this time would therefore have the least impact on the population size at Devils Hole. When transferred to AMFCF, the eggs are exposed to anti-fungal, anti-bacterial, and anti-parasite treatments. They are reared in the aquarium until adulthood, at which point they are transferred to the large refuge tank. This procedure is also followed for eggs laid in the refuge tank. While efforts have been made to remove the predaceous beetle Neoclypeodytes cinctellus from the captive population's tank to lessen its depredation on eggs, it has not been removed from Devils Hole. It is unknown how removal of the species could affect the Devils Hole ecosystem, and the number of beetles in Devils Hole is less than in the tank hosting the captive population.

Spring 2019 count..
As of 2021, the efforts of the Ash Meadows Fish Conservation Facility have been considered "very successful" in maintaining a refuge population. At least fifty captive fish populated the refuge as of 2019, with an additional 10–20 in propagation tanks.
A 2014 study ascertained that the Devils Hole pupfish had a 26–33% chance of becoming extinct in the next twenty years. From 1970 through 1996, the average population was 324. Population highs were recorded in 1980, 1990, and 1995 at counts of 541–548 individuals. Since 2005, the population at Devils Hole has been below 200 individuals, although the population fluctuates depending on the season. Millions of dollars have been spent conserving the Devils Hole Pupfish. The construction of the Ash Meadows Fish Conservation Facility alone, which opened in 2013, was estimated to cost $4.5 million. Conservation efforts from January 2006 to May 2007 were $750,000. The legal case over the rights to extract groundwater concluded that the Cappaert family, who invested $7 million into opening a ranch in the area, could no longer withdraw the same amount of water. The Cappaert family's attorney decried that the Supreme Court had chosen the interests of a fish over people, and a newspaper editor from nearby Pahrump threatened to dump a pesticide into Devils Hole to kill them all. In response to bumper stickers that read "Save the Pupfish" distributed by the Desert Fishes Council, Nye County Commissioner Robert Rudd produced bumper stickers that said "Kill the Pupfish". The Cappaert family sold the ranch in the late 1970s.

The age of the species is subject to considerable debate, with analyses recovering starkly different figures. Devils Hole was formed around 60,000 years ago, with some researchers assuming the pupfish has existed in isolation for 10,000–20,000 years. How it colonized Devils Hole is unknown; hypotheses include arriving via subterranean waters or over dry land. As Native Americans used pupfish species as food, it has been speculated that they introduced the pupfish to Devils Hole, intentionally or not. Its divergence from a common ancestor with C. nevadensis mionectes was estimated at 217–2530 years in one study. Two studies, each based on independent genetic datasets, estimated that this species may have first colonized the hole within the past 1,000 years, but another suggested the species is as old as 60,000 years. These estimates depend heavily on knowledge of the mutation rate in this species, which is unknown, but is predicted to be one of the highest for any vertebrate due to its small population size.

.webp)
The pupfish is the rarest fish on Earth having dwindled down to a population of just 19 individuals this species was close to extinction..
A biologist with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service observes captive Devils Hole pupfish. / USFWS

The family and friends of the missing divers were photographed at the site three days after the dive, when the rescue attempts were halted.
Associated Press
.jpg)
On March 20, 2012, a 7.4-magnitude earthquake in Oaxaca, Mexico, some 2,000 miles (3,200 km) away and centered roughly 12 miles (19 km) below the surface, caused an undulating 4 feet (1.2 m) rise and fall of the cavern waters, as appreciated by researchers working at Devil's Hole at the time. This provided further evidence that the Devil's Hole cave system was connected not only to the Death Valley Regional Groundwater Flow System, but possibly to even further-reaching underground water systems. The 1991 USGS dive team described the Devil's Hole as a "skylight" into the water table.
In 1965, Paul Giancontieri, a teenager who had jumped the fence with friends to go SCUBA diving the hole, did not come back up. Another, David Rose, went down to find him, but did not come back up either. Later efforts by five divers to find their bodies were unsuccessful. On June 20, 1965, during the second dive of a rescue and then body recovery mission, Jim Houtz with his dive partner dropped a weighted depth line to a depth of 932 feet (284 m) from the start of this opening, without hitting the bottom of the chamber below. Due to the strong current, the small size of the entrance, and the unknown depth of the cavern below, which Houtz termed the "Infinity Room", Jim and his partner chose not to explore this Infinity Room. This mission did, however, confirm that the Infinity Room of Devil's Hole, and the cavern system itself, has a depth of at least 1,247 feet (380 m) from the surface.
A subsequent USGS exploration into Devil's Hole in 1991 by Alan Riggs, Paul DeLoach, and Sheck Exley entered what they found out to be a narrow tube rather than an 'Infinity Room' at 315 feet (96 m), descending to a depth of 436 feet (133 m). The team reported being able to see down to a depth of some 500 feet (150 m), without visualizing the bottom of the cavern.

Sheck Exley with Mary-Ellen-Eckhoff-

Paul DeLoach

Ash Meadows National Wildlife Refuge

Ash Meadows Wildlife Refuge - Nevada - Prehistoric Pup Fish - Outlaw Cabin - Tom Green - Van Life

An EPIC drive to Death Valley (Ash Meadows, Wild Burros, Rhyolite GHOST town, & Titus Canyon!)
Ash Meadows Wildlife Refuge - Nevada - Prehistoric Pup Fish - Outlaw Cabin - Tom Green - Van Life
An EPIC drive to Death Valley (Ash Meadows, Wild Burros, Rhyolite GHOST town, & Titus Canyon!)


Fairbanks pool - In Southwestern Nevada, there’s a place where some of the purest, clearest, cleanest and most pristine water bubbles to the surface. Shocked? You shouldn’t be. As I’ve discussed before, large swathes of Eastern California used to be glacial lakes, such as where present day Trona and the Trona Pinnacles are located. There’s also an oasis in the former town of Zzyzx, and groundwater at Salt Creek in Death Valley and Badwater. Even cooler, Death Valley has salt pools that randomly appear and disappear across the Valley floor proper in random locations (one of the more accessible pools is currently located by the Devil’s Golf Course, but it is closing – slowly!). When you look at it like this, through the lens of time, geologic change, as well as the interconnected nature of the environment, crystal clear desert oases really aren’t that surprising.
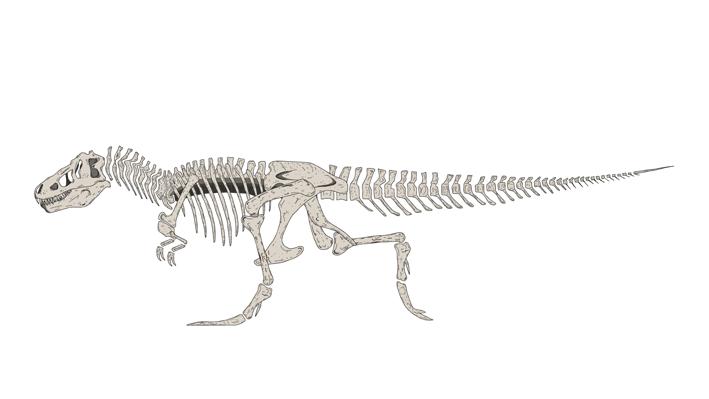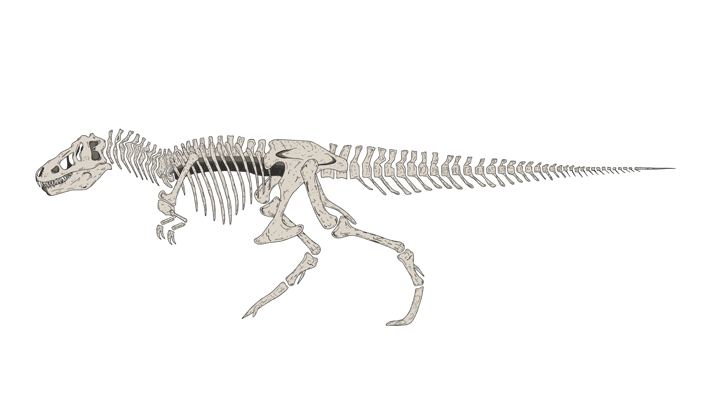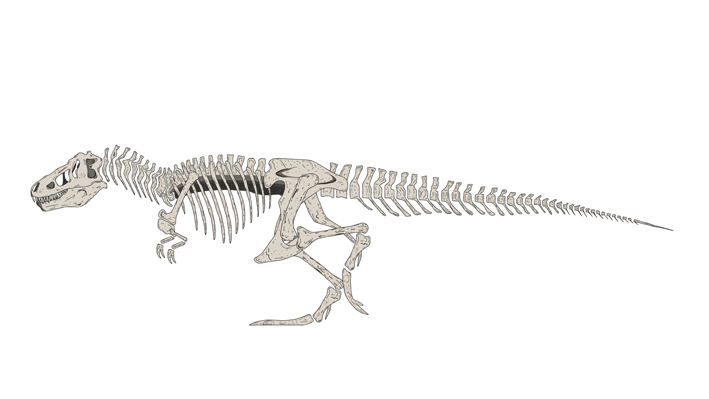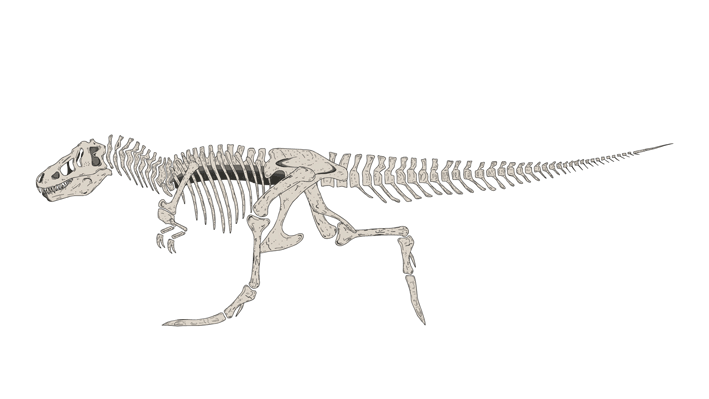
Sue is the nickname given to FMNH PR 2081, which is one of the largest, most extensive, and best preserved Tyrannosaurus rex specimens ever found, at over 90 percent recovered by bulk. FMNH PR 2081 was discovered on August 12, 1990, by American explorer and fossil collector Sue Hendrickson, and was named after her. After ownership disputes were settled, the fossil was auctioned in October 1997 for US$8.3 million, the highest amount ever paid for a dinosaur fossil until October 7, 2020 when T. rex Stan was auctioned for US$31.8 million. Sue is now a permanent feature at the Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago, Illinois

Sue Hendrickson and Pete Larson pose at the site where SUE was excavated.
SUE HENDRICKSON’S PHOTO © BLACK HILLS INSTITUTE OF GEOLOGICAL RESEARCH

Waking the T. Rex: The Story of Sue (2010)
Waking the T. Rex: The Story of Sue (2010)
During the summer of 1990, a group of workers from the Black Hills Institute, located in Hill City, searched for fossils at the Cheyenne River Indian Reservation in western South Dakota near the city of Faith. By the end of the summer, the group had discovered Edmontosaurus bones and was ready to leave. However, a flat tire was discovered on their truck before the group could depart on August 12. While the rest of the group went into town to repair the truck, Sue Hendrickson decided to explore the nearby cliffs that the group had not checked. As she was walking along the base of a cliff, she discovered some small pieces of bone.

This land of sprawling prairies and abundant waters is home to the Cheyenne River Sioux Tribe or Cheyenne River Lakota Nation (Oyate), which is made up of parts of four of the traditional seven bands of the Lakota Nation: Plants by the Water or Mnicoujou, Sans Arc or Itazipco, Black Foot or Sihasapa, and Two Kettles or Oohenumpa. These bands speak Lakota.
She looked above her to see where the bones had originated, and observed larger bones protruding from the wall of the cliff. She returned to camp with two small pieces of the bones and reported the discovery to the president of the Black Hills Institute, Peter Larson. He determined that the bones were from a T. rex by their distinctive contour and texture. Later, closer examination of the site showed many visible bones above the ground and some articulated vertebrae.

The Tragic Real-Life Story Of Sue The T-Rex
The Tragic Real-Life Story Of Sue The T-Rex
The crew ordered extra plaster and, although some of the crew had to depart, Hendrickson and a few other workers began to uncover the bones. The group was excited, as it was evident that much of the dinosaur had been preserved. Previously discovered T. rex skeletons were usually missing over half of their bones. It was later determined that Sue was a record 90 percent complete by bulk, and 73 percent complete counting the elements. Of the 360 known T. rex bones, around 250 have been recovered. Scientists believe that this specimen was covered by water and mud soon after its death, which prevented other animals from carrying away the bones. Additionally, the rushing water mixed the skeleton together.

The Black Hills Institute of Geological Research, Inc. (BHI) is a private corporation specializing in the excavation and preparation of fossils, as well as the sale of both original fossil material and museum-quality replicas. Founded in 1974 and based in Hill City, South Dakota, the company is most famous for excavating and selling replicas of some of the most complete specimens of Tyrannosaurus rex, including "Sue", "Stan" and "Trix".
When the fossil was found, the hip bones were above the skull and the leg bones were intertwined with the ribs. The large size and the excellent condition of the bones were also surprising. The skull was 1,394 mm (54.9 in) long, and most of the teeth were still intact. After the group completed excavating the bones, each block was covered in burlap and coated in plaster, followed by a transfer to the offices of the Black Hills Institute, where they began to clean the bones.

Maurice Williams

SUE the dinosaur - Dating back to the Cretaceous period—about 67 million years ago—this massive predator lived to the upper end of the life expectancy of a T. rex, about 28 years. (How do we know? Dinosaur bones have growth rings, just like trees. After examining these rings, scientists also determined that SUE had an adolescent growth spurt—gaining as much as 4.5 pounds per day—and reached full size at age 19.)



April 14, 1926 - May 16, 2011
Funeral services for Maurice Williams, age 85, of Faith formerly of Dupree will be 10 AM, MT Thursday, May 19, 2011 at the Dupree United Church of Christ. Burial will be in the Dupree Cemetery under the direction of Kesling Funeral Home of Mobridge. Visitation will be one hour prior to services. Maurice passed away Monday, May 16, 2011 at the Rapid City Hospice House in Rapid City.
Maurice A. Williams was born on April 14, 1926, in Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada, to Christopher and Kate (Aspdin) Williams. He grew up on the family ranch near Red Elm, SD. He attended grade schools at Lantry, Butler, and Red Elm. The family moved to Dupree so Maurice and his brother, Ramon, could attend high school. After he graduated, he joined the US Navy and served his country in World War II. After he returned home, he attended college at Colorado A&M in Fort Collins, CO. In 1950, he received a Bachelor of Science degree in Animal Husbandry. Maurice then worked for a short time for the Bureau of Indian Affairs on the Yankton Reservation at Greenwood, SD.
He returned to his home near Red Elm and continued to help his parents ranch. Maurice's mother always told him, "If you want to ranch, buy your own land." With hard work and determination, Maurice did just that. He began acquiring land, buying cattle, and built the ranch of his dreams. During this time, he also taught the ranching business to veterans for several years.
In 1957, Maurice met and married Darlene Zephier, and to this union had four children. He began working for the Bureau of Indian Affairs in Eagle Butte, SD, and continued, with the help of his wife and children, to build the ranch he always dreamed of.
Maurice was a man who worked hard to achieve his goals, and he did that with the wise use of money and fierce determination. He set out to build a legacy for his children. He never took the credit for his accomplishments as he would often tell his wife, "Mother, without the Lord we wouldn't have what we have today. We've got to remember to thank the Lord for everything he has given us."
He is survived by his wife, Darlene, of 54 years, four children, Sandra Williams Luther (James), Brady Williams, Jackie Schwartz (Mike), and Carson Williams (Samantha), 10 grandchildren, and one great grandson.
Maurice was preceded in death by his parents Chris and Kate Williams, and his brother Roman.

Soon after the fossils were found, a dispute arose over their legal ownership. The Black Hills Institute had obtained permission from the owner of the land, Maurice Williams, to excavate and remove the skeleton, and had paid Williams US$5,000 for the remains. Williams later claimed that the money had not been for the sale of the fossil and that he had only allowed Larson to remove and clean the fossil for a later sale. Williams was a member of the Sioux tribe, and the tribe claimed the bones belonged to them. However, the property where the fossil had been found was held in trust by the United States Department of the Interior.
SUE’s sex is unknown; this T. rex is named for Sue Hendrickson, who discovered the dinosaur in 1990 during a commercial excavation trip north of Faith, South Dakota.
In 1992, the FBI and the South Dakota National Guard raided the site where the Black Hills Institute had been cleaning the bones and seized the fossil, charging Larson on 158 points. The government transferred the remains to the South Dakota School of Mines and Technology, where the skeleton was stored until the penal and civil legal disputes were settled. The United States Senate voted to not confirm the appointment of Kevin Schieffer as United States Attorney for the District of South Dakota after his controversial handling of the penal case.

Sue the Dinosaur Finds a New Home in Chicago - Decades TV Network
Sue the Dinosaur Finds a New Home in Chicago - Decades TV Network

Peter LarsonCredit...Lionsgate
In 1996, Larson was sentenced to a two-year prison sentence after being convicted on charges not directly related to Sue. After a lengthy civil case, the court decreed that Maurice Williams retained ownership, because as a beneficiary, he was protected by the law against an impulsive selling of real property, and the remains were returned in 1995. Williams then decided to sell the remains, and contracted with Sotheby's to auction the property. Many were then worried that the fossil would end up in a private collection where people would not be able to observe it. The Field Museum in Chicago was also concerned about this possibility, and decided to attempt to purchase Sue. However, the organization realized that they might have had difficulty securing funding and requested that companies and private citizens provide financial support.
The California State University system, Walt Disney Parks and Resorts, McDonald's, Ronald McDonald House Charities, and individual donors agreed to assist in purchasing Sue for the Field Museum. On October 4, 1997, the auction began at US$500,000; less than ten minutes later, the Field Museum had purchased the remains with the highest bid of US$7.6 million. The final cost was US$8,362,500.

Sue has a length of 12.3–12.4 meters (40.4–40.7 ft) along the centra, stands 3.66–3.96 meters (12–13 ft) tall at the hips, and has been estimated at between 8.4–14 metric tons (9.26–15.4 short tons) as of 2018. In 2011, other size estimates were between 9.5–18.5 metric tons (10.5–20.4 short tons), although the authors stated that their upper and lower estimates were based on models with wide possible errors, and that they "consider them [these extremes] to be too skinny, too fat, or too disproportionate". A further estimate portrayed a leaner build, placing the specimen at 8.4 metric tons (9.3 short tons), while older estimates have placed this specimen at 5.7–6.4 metric tons (6.3–7.1 short tons) in weight. Displayed separately from the whole body, the skull weighs 272 kg (600 lb). The longest known gastralium (belly rib) among theropods, measuring about 90 centimeters (3.0 ft), is known from this specimen. Sue also has the longest known pubis currently measured among the Cretaceous theropods, measuring roughly 136 centimeters (4.46 ft). Sue is one of the largest Tyrannosaurus specimens, with "Scotty": RSM P2523.8 the only specimen with a similar size.

The Field Museum hired a specialized moving company with experience in transporting delicate items to move the bones to Chicago. The truck arrived at the museum in October 1997. Two new research laboratories funded by McDonald's were created and staffed by Field Museum preparators whose job was to slowly and carefully remove all the rock, or "matrix", from the bones. One preparation lab was at the Field Museum itself, the other was at the newly opened Animal Kingdom in Disney World in Orlando. Millions of visitors observed the preparation of Sue's bones through glass windows in both labs. Footage of the work was also put on the museum's website. Several of the fossil's bones had never been discovered, so preparators produced models of the missing bones from plastic to complete the exhibit. The modeled bones were colored in a purplish hue so that visitors could observe which bones were real and which bones were plastic. The preparators also poured molds of each bone. All the molds were sent to a company outside Toronto to be cast in hollow plastic. The Field Museum kept one set of disarticulated casts in its research collection. The other sets were incorporated into mounted cast skeletons. One set of the casts was sent to Disney's Animal Kingdom in Florida to be presented for public display. Two other mounted casts were placed into a traveling tour that was sponsored by the McDonald's Corporation.

Once the preparators finished removing the matrix from each bone, it was sent to the museum's photographer who made high-quality photographs. From there, the museum's paleontologists began the study of the skeleton. In addition to photographing and studying each bone, the research staff also arranged for CT scanning of select bones. The skull was too large to fit into a medical CT scanner, so Boeing's Rocketdyne laboratory in California agreed to let the museum use their CT scanner that was normally used to inspect space shuttle parts.
McDonalds packaging for SUE the T-rex

Big dig: Peter Larson and his team uncovering the skull in 1990
Sue the T-Rex was a fighter some 65 million years ago - Close examination of the bones revealed that Sue was 28 years old at the time of death—the oldest T. rex known until Trix was found in 2013. A Nova episode said that the death occurred in a seasonal stream bed, which washed away some small bones. During life, this carnivore received several injuries and suffered from numerous pathologies. An injury to the right shoulder region of Sue resulted in a damaged shoulder blade, a torn tendon in the right arm most likely due to a struggle with prey, and three broken ribs. This damage subsequently healed (though one rib healed into two separate pieces), indicating Sue survived the incident. The left fibula is twice the diameter of the right one, likely the result of infection. Original reports of this broken bone were contradicted by the CT scans which showed no fracture.[citation needed] The injuries to both the left fibula and the fused c26 and c27 caudal vertebrae show signs consistent with the bone infection osteomyelitis.

A dino named Sue: the 12.3m-long Tyrannosaurus rex specimen as it now stands in the Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago. Photograph: Dallas Krentzel. Wikipedia.
Multiple holes in the front of the skull were originally thought to be either from a bacterial infection or bite marks by some other tyrannosaur. A subsequent study found these to be areas of parasitic infection instead, possibly from an infestation of an ancestral form of Trichomonas gallinae, a protozoan parasite that infests birds and ultimately leads to death by starvation due to internal swelling of the neck. Damage to the back end of the skull was interpreted early on as a fatal bite wound. Subsequent study by Field Museum paleontologists found no bite marks. The distortion and breakage seen in some of the bones in the back of the skull was likely caused by post-mortem trampling. Some of the tail vertebrae are fused in a pattern typical of arthritis due to injury. The animal is also believed to have suffered from gout. Scholars debate exactly how the animal died; the cause of death is ultimately unknown.


After the bones were prepared, photographed and studied, they were sent to New Jersey where work began on making the mount. This work consists of bending steel to support each bone safely and to display the entire skeleton articulated as it was in life. The real skull was not incorporated into the mount as subsequent study would be difficult with the head 4 m (13 ft) off the ground. Parts of the skull had been crushed and broken and thus appeared distorted. This also provides scientists with easier access to the skull as they continue to study it. The museum made a cast of the skull, and altered this cast to remove the distortions, thus approximating what the original undistorted skull may have looked like. The cast skull was also lighter, allowing it to be displayed on the mount without the use of a steel upright under the head. The original skull is exhibited in a case that can be opened to allow researchers access for study. Originally, the Field Museum had plans to incorporate Sue into their preexisting dinosaur exhibit on the second floor, but had little left in their budget to do so after purchasing it. Instead, the T. rex was put on display near the entrance on the first floor of the museum where it would remain for the next 18 years. Sue was unveiled on May 17, 2000, with more than 10,000 visitors. John Gurche, a paleoartist, painted a mural of a Tyrannosaurus for the exhibit.


Exploring the Chicago Field Museum
Exploring the Chicago Field Museum 2022.
The Assault
At 7:30 a.m. on May 14, 1992, something happened which will forever alter the way every citizen of Hill City, South Dakota, old enough to assimilate it feels about government. For the school children who witnessed it, it may well become the defining moment in their lives. It was, in reality, just another day on which officers of the United States Government violated their trust. But on that spring morning it happened so brutally and so publicly that an entire town is still stunned. That morning, acting on the orders of acting U.S. Attorney for South Dakota Kevin Schieffer, 9 FBI agents, 4 National Park rangers, 2 agents from the Department of Interiors office of Inspector General, 1 Bureau of Indian Affairs agent, 1 South Dakota Highway Patrolman, 1 Pennington County Deputy Sheriff, and several paleontologists or other scientists (information from FBI agent Charles Draper) executed a search and seizure warrant, which had been signed the previous afternoon by U.S. District Court Judge Richard Battey of Rapid City.

IN THE MATTER OF THE INVESTIGATION OF THE REMOVAL OF FOSSILS FROM INDIAN LANDS...on the premises ... known as the Black Hills Institute of Geological Research, Inc. ... there is now being concealed certain property, namely,(1) all the fossil remains of one tyrannosaurus rex dinosaur skeleton (commonly referred to as Sue) ..., as well as other fossil specimens as further set forth in detail in Exhibit A and the affidavits in support of this application for a search warrant, which ... were taken from a ... site on the property of Maurice Williams, [legal description of site], which property is held in trust by the United States of America;(2) all the papers, diaries, notes, photographs, including slides, memoranda, tape recordings, videotapes, maps, butcher paper and samples or other records relating to the excavation of the tyrannosaurus rex (Sue) and the other ... specimens;(3) all other fossil remains taken from the above Maurice Williams excavation site, as identified in the notes, photographs ... or other records seized pursuant to paragraph 2, above, and;(4) all papers, diaries, notes, ... relating to a separate excavation site on land owned by the Cheyenne River Sioux Tribe, and held in trust by the United States described as [legal description] and any fossil specimens removed from the second excavation site.... and as I am satisfied that there is probable cause to believe that the property so described is being concealed on the person or premises above- described and the grounds for application for issuance of the search warrant exist ...Exhibit A contained a list.1. Parts of duckbilled dinosaurs.2. An ostrich-like bird.3. A slightly disarticulated turtle skull.4. Crocodile bones.5. Parts of other tyrannosaurus dinosaurs.

Sue, Peter Larson/Photo: Ray Pride

VIDEO: Dinosaurs take the track in viral T-Rex races
VIDEO: Dinosaurs take the track in viral T-Rex races
The premises secured (FBI agent Draper: "We didn't know what we were gonna run into".), the search and seizure begun, Kevin Schieffer arrived from Rapid City (about 30 miles away) at about 10:30 a.m. As Pete Larson, one of the owners of BHIGR put it, "I knew we were in trouble when the [acting] U.S. Attorney arrived at the seizure wearing makeup".
Hill City is a logging town with a population of 550 located more or less in the center of the Black Hills of South Dakota. Its major annual celebration is a lumberjack festival known as Heart of the Hills Day. It boasts a great little restaurant, the Alpine Inn, which offers two meals a large filet and a small filet; a collection of M. L. Warne's mounted big game trophies collected around the world called "The Call of the Wild"; and the 1880's Train, a steam engine from the last century which offers rides for tourists. In addition, Hill City's main street, a three-block section of U.S. Highway 385, contains several stores bristling with souvenirs and t-shirts. The town is really alive only from Memorial Day through Labor Day the tourist season. The Black Hills Institute of Geological Research located itself in Hill City's vacant American Legion Hall and Hill City Auditorium, a WPA project constructed in the late thirties, in the fall of 1979.
On the morning of May 13 [1992] a group of elementary school children went to the Institute to present its owners with the proceeds of a bake sale $61.28 for the fund which had been started to build a new geological/paleontological museum whose centerpiece was to have been Sue, the largest and most complete Tyrannosaurus rex fossil ever found. The next morning found the place swarming with grim-faced men wearing blue jackets bearing the legend FBI in foot-tall yellow letters, along with a variety of other federal, state, and local agents.Shortly, several South Dakota National Guard troops, trucks, and forklifts arrived to begin loading and transporting the huge tonnage of specimens, much still encased in its sandstone tombs.




.jpg)


Footprints of Late Cretaceous duck-billed dinosaurs or “hadrosaurs” were named Hadrosauropodus, what means “hadrosaur track”. They are relatively common in the Upper Cretaceous of North America. In Utah, they can be found among the rich material from Blackhawk Formation of Price area. However, these tracks are the isolated casts from the coal mines and have not been described in detail. The most recent find came from Castlegate Sandstone of the Thompson Pass area in Utah and seems to be Hadrosauropodus made by juvenile hadrosaur.
It was a herbivorous dinosaur, eating plants. Its skull permitted a grinding motion similar to chewing. Its teeth were continually replacing and packed into dental batteries with hundreds of teeth. It used its duck-billed beak to crop plant material. It was built to walk on all fours as well as on two legs. Parasaurolophus was distinguished by the long, hollow cranial crest, curved structure longer than the rest of skull, which protruded from the rear of the head. The crests of male parasaurophuses were longer the those of females. One current theory is that these tubes might have produced blast of sound, when filled with air.
We know SUE the T-Rex's last meal was a duckbill dinosaur. There were other parts of other T-Rexes in there, there was a tibia and fibula that were both bitten in half with marks on the bones from teeth and micro-scratches where the serrations matched, so we know it was bitten in half by a T-Rex, whether it was Sue or someone who attacked Sue. We don’t know. Frontal bones from an even smaller T-Rex were in there, too.” Paleontologist: Peter Larson

The Balaenognathus maeuseri's jaw 'was really long and lined with small, fine, hooked teeth' CREDIT: Megan Jacobs/PA

Scientists were excavating a large block of limestone containing crocodile bones when they came across the fossil..
A new species of dinosaur that had hundreds of small hooked teeth and ate in a similar way to ducks and flamingos has been discovered. The fossil of the nearly complete Balaenognathus maeuseri, part of the pterosaur family, was discovered accidentally in a Bavarian quarry in Germany while scientists were excavating a large block of limestone containing crocodile bones. Since the first pterosaur was discovered in Bavarian limestone in the 18th century, hundreds of remains of the flying reptiles have been unearthed, making the quarries of the Franconian Jura one of the richest pterosaur localities in the world. The research was led by Prof David Martill of the University of Portsmouth, Hampshire, and involved palaeontologists from England, Germany and Mexico.
Prof Martill said: "The nearly complete skeleton was found in a very finely layered limestone that preserves fossils beautifully. "The jaws of this pterosaur are really long and lined with small, fine, hooked teeth, with tiny spaces between them like a nit comb. "The long jaw is curved upwards like an avocet and at the end it flares out like a spoonbill. There are no teeth at the end of its mouth, but there are teeth all the way along both jaws right to the back of its smile. "What's even more remarkable is some of the teeth have a hook on the end, which we've never seen before in a pterosaur ever. "These small hooks would have been used to catch the tiny shrimp the pterosaur likely fed on - making sure they went down its throat and weren't squeezed between the teeth."

The animal likely dabbled as it waded through shallow lagoons, sucking in tiny water shrimps and copepods and then filtering them out through its teeth in the same way as ducks and flamingos.
The name "Balaenognathus" roughly translated means whale mouth because of its filtering feeding style, while the specific name "maeuseri" is in honour of co-author Matthias Mauser, who died during the writing of the paper.
Prof Martill said: "Matthias was a friendly and warm-hearted colleague of a kind that can be scarcely found. In order to preserve his memory, we named the pterosaur in his honour."
Duck-Billed Dinosaur.
The paper, A new pterodactyloid pterosaur with a unique filter-feeding apparatus from the Late Jurassic of Germany, is published in Palaontologische Zeitschrift.
The specimen is currently on display in the Bamberg Natural History Museum in Germany.

The Hollow-Crested Hadrosaurids or Lambeosaurinae are the first subfamily of duck-billed Hadrosaurids. This class of Dinosaurs possesses a conspicuous head crest above their head, making them peculiar and easy to identify. This family also consists of more than ten recognized subgroups.
The prominent crest of the Lamb5eosaurine had hollow air chambers that many paleontologists suggest as part of nasal passages, used to produce sounds, and simultaneously serves as a visual display of some sort. It was also believed that these crests were used to breathe fire, but this opinion has been scientifically dismissed.
This is opposed to the sister subfamily Saurolophinae which had solid crests or no crest. The two major species worthy of note in the Lambeosaurinae subfamily are Parasaurolophus and Lambeosaurus.
The-Hollow-Crested-Hadrosaurids

A large plant-eating Dinosaur that lived in the late Cretaceous period. Its name means “Helmet Lizard.” Just like other duck-billed Dinosaurs, Corythosaurus has large numbers of teeth, in this case, behind its jaws, which it uses to crush plant matter. Its bony crest contained a nasal passage and might have been a communication device. Different skeletons of Corythosaurus have belonged to about seven different species. Only one species is, however, recognized currently because a comparison of more than 20 skulls has proved that the crest changes as it grows larger.
Four-corythosaurus-in-the-forest

Image-of-Maiasaura
Maiasaura were large herbivores, reaching a known height of 9 meters (30ft). Their beaks were flat, which is a characteristic of hadrosaurids. They could walk on both two feet (bipedal) and four feet (quadrupedal). The juveniles under four years utilized only their hind legs and transitioned into a quadrupedal walking mode as they grew larger.
This class of Hadrosaurids, as stated earlier, possessed no crests. Thus, they did not have many defensive features. However, they had muscular tails, which were very useful for defense. It has also been suggested that the large sizes of their herds served as a means of protection. Their herds were huge, consisting of up to 10,000 Dinosaurs.

image-of-Gryposaurus
Gryposaurus (meaning “hooked-nosed (Greek grapes) lizard”; sometimes incorrectly translated as “griffin (Latin gryphus) lizard”) was a genus of duckbilled dinosaur that lived about 83 to 74 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period (late Santonian to late Campanian stages) of North America.
Gryposaurus is based on specimen NMC 2278, a skull and partial skeleton collected in 1913 by George F. Sternberg from what is now known as the Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, along the Red Deer River. This specimen was described and named by Lawrence Lambe shortly after that, Lambe drawing attention to its prominent crest. In fact, the distinctive crest was particularly unusual.
There are three species of Gryposaurus named, and research is still ongoing on discovering new species. The three named species of Gryposaurus differ in details of the skull and lower jaw. The prominent nasal arch found in this genus is formed from the paired nasal bones.
In profile view, they rise into a rounded hump in front of the eyes, reaching a height as tall as the highest point of the back of the skull. The skeleton is known in great detail, making it a useful reference point for other duckbill skeletons.
Speaking of the unique nasal arch of Gryposaurus, like other cranial modifications in duckbills, it may have been used for a variety of social functions, such as identification of sexes or species and social ranking.
It could also have functioned as a tool for broadside pushing or butting in social contests, and there may have been inflatable air sacs flanking it for both visual and auditory signaling. Gryposaurus was a herbivore and laid eggs.

This group of hadrosaurs do not fall under either subfamily of the duck-billed dinosaurs but belong to the Hadrosauridae family because they possess all the common features, as well as the rostral duckbill bones. Researchers believe that they also have a common ancestry with the family.
The term ‘Basal’ in biological terms has to do with being ancestral. Thus, they are the oldest members of the entire duck-billed Dinosaurs. The most prominent member of this group happened to be the first to be discovered in North America, the Hadrosaurus foulkii.